经常接触的是二叉树, 对四叉树或者八叉树仅仅是有所耳闻, 知道是干嘛的:
四叉树广泛应用于图像处理、空间数据索引、2D中的快速碰撞检测、存储稀疏数据等,而八叉树(Octree)主要应用于3D图形处理。对游戏编程,这会很有用。
但从未自己实现过, 今天来简单地实现一下四叉树的构造, 题目来源于LeetCode 427. 思路很简单, 其实就是递归.
/*
// Definition for a QuadTree node.
class Node {
public:
bool val;
bool isLeaf;
Node* topLeft;
Node* topRight;
Node* bottomLeft;
Node* bottomRight;
Node() {}
Node(bool _val, bool _isLeaf, Node* _topLeft, Node* _topRight, Node* _bottomLeft, Node* _bottomRight) {
val = _val;
isLeaf = _isLeaf;
topLeft = _topLeft;
topRight = _topRight;
bottomLeft = _bottomLeft;
bottomRight = _bottomRight;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* construct(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int N=grid.size();
if(N==0) return nullptr;
return DFS(grid,0,0,N);
}
Node* DFS(vector<vector<int>>& grid,int x,int y,int N)
{
if(N==1) return new Node(grid[x][y]==1?true:false,true,nullptr,nullptr,nullptr,nullptr);
N/=2;
Node* topLeft=DFS(grid,x,y,N);
Node* topRight=DFS(grid,x,y+N,N);
Node* bottomLeft=DFS(grid,x+N,y,N);
Node* bottomRight=DFS(grid,x+N,y+N,N);
if(topLeft->isLeaf && topRight->isLeaf && bottomLeft->isLeaf && bottomRight->isLeaf && topLeft->val==topRight->val && topRight->val==bottomLeft->val && bottomLeft->val==bottomRight->val)
{
bool val=topLeft->val;
delete topLeft;
delete topRight;
delete bottomLeft;
delete bottomRight;
return new Node(val,true,nullptr,nullptr,nullptr,nullptr);
}
else
return new Node(true,false,topLeft,topRight,bottomLeft,bottomRight);
}
};
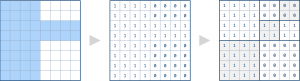
一开始忘记了合并四个相同值的叶子节点, 其实是有必要的, 因为这可以节省一些内存空间, 整个算法时间复杂度与四叉树的深度有关, 大概是O(lgN). 类似地, 八叉树也是同样的道理, 只不过相比四叉树而言每个节点至多多了四个分叉罢了~